Shin Lee, Julie Kim, Josh Koo
PDF Report
Title: Facebook News Topics
Contact: joshuakoo2019@u.northwestern.edu
Course: Machine Learning: EECS 349 at Northwestern University
Abstract
We wanted to apply machine learning techniques to classify Facebook News topics and give news recommendation for users who are interested in certain topics. For example, if an individual is active on Facebook and likes to read news about cars, we wanted our machine learning techniques to classify whether news articles are related to cars and give recommendations accordingly. Using programming and analytical methods, we wrote scripts to scrape data from Facebook Trending News, conducted pre-processing on our collected data, and analyzed the data with Weka.
Introduction
Motivation
The project tackles the broad task of analyzing news articles and determining whether or not the topic of the article is based on tech companies, an arbitrarily chosen topic to illustrate our objective of customizable news recommendations. To be specific, our project deals with analyzing news articles under the Facebook “Trending” news column. This specific task is important because of how relevant tech-related discussion is in recent times and because of how widespread the usage of Facebook is, which allows for easy news distribution. It is crucial for social media news platforms to give relevant news topics that are interesting to each user. Ultimately our project aims to allow easy distribution of important tech-related news articles relevant to certain users on Facebook.
Methodology
Data
To collect our data, we wrote scraping scripts in Python 3.6.4 and Selenium, a user interface (UI) automation tool that automates UI testing. Our raw data consisted of roughly 50,000 data each with the 7 attributes listed below:
- Type: The broad topic (top trends, politics, science and technology, sports, or entertainment)
- Title: Title of news article
- Description: The short description located under the title
- Trend Link: The link that redirects the user when the trending article is clicked. The link redirects the user to a compilation of news on a Facebook page.
- Rank: Where the article is ranked in the trending list
- Scrape ID: An integer to keep track of which round of scraping the data is collected from
- Timestamp: The exact time and day the data was collected (YY-MM-DD HH-MM-SS)
Type was used to distinguish the different topics during the analysis, investigating the top articles for all five topics. Title and description were collected for detail on each trending news article. The trend link was used to uniquely identify each article. Rank was collected to discover where in each list certain articles were placed and whether they moved up or down the list. Scrape ID was used with trend link to uniquely identify articles for the whole dataset. Timestamp was used to keep track of the time and date the data was collected, which was critical when analyzing trending behavior at different days of the week.
We needed to preprocess our data in order to address our problem, so we removed duplicate news articles by filtering by description and went in by hand to add a classification attribute based on whether the article is related to our chosen topic or not. There was a very small percentage of articles that were relevant to our topic. After this preprocessing, we used Weka to analyze our data with different classifiers and recorded overall accuracy, along with precision and recall values for the “yes” (i.e. related to our topic) classification.
We tried several learners via Weka, the exhaustive list being: Naive Bayes, Logistic Regression, IBk, J48, Simple Logistic, and Bayes Net.
Results
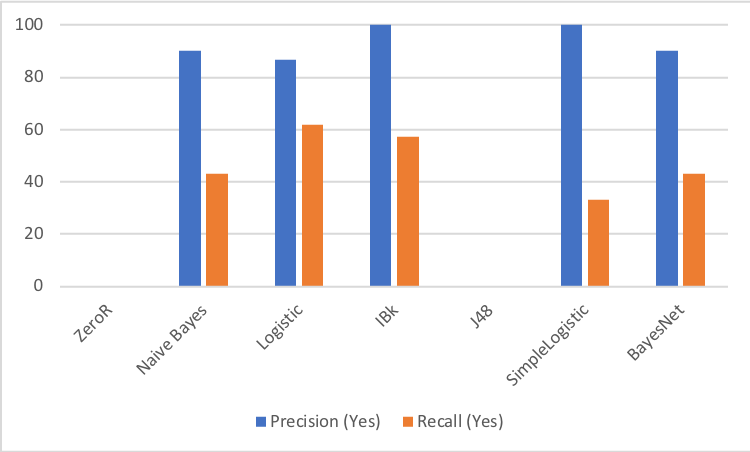 Figure 1. Precision and Recall Results for Trained Models on Test Data
Figure 1. Precision and Recall Results for Trained Models on Test Data
The figure above depicts the results that various machine learners achieved on our data. Although we recorded accuracy, precision, and recall, the above figure reports precision and recall, which were the values we focused on. We believe precision and recall are the most important, more so than accuracy. Our results, in terms of accuracy, performed well across the board with different machine learners. This is not very informative, however, because given that the media covers a large variety of topics and thus most news articles are not about tech companies, the machine learners can achieve high accuracy by classifying most articles as irrelevant to our topic of tech companies. For example, the accuracy scores for ZeroR and J48 were only lower than the others by a small amount, but they achieved 0% precision and recall, because they classified every news article as the majority classification.
Therefore, we judged performance by focusing on precision and recall. From our Weka results, the machine learners with the best precision were Simple Logistic and IBk, and the learners with the best recall were Logistic and IBk. As far as important features go, by looking at an unpruned decision tree, we found that title was the most important. This lead to the key finding that the classifications primarily operate by identifying keywords in the article titles, and news articles related to large tech companies often have the names of the companies in the title.
Sources
https://www.recode.net/2017/9/7/16270900/social-media-news-americans-facebook-twitter
Website: https://shinandruth.github.io/Facebook-News-Topics/